Skip to content
- Disease: Fasciolopsiasis
- Habitat in human: Small intestine
- Definitive host: Humans and pigs
- 02 Intermediate hosts: Snails and aquatic vegetation
- Diagnosis of infection: Microscopic examination of faeces to detect eggs
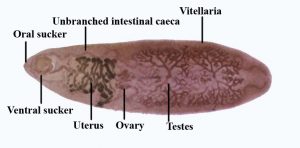
Morphological Features
- Size: 20-75 mm in length and a width of 8-20 mm – Largest intestinal fluke of human
- Flattened and leaf-shaped, with a spiny tegument covering body
- Has oral sucker and an acetabulum. But no oral cone or shoulders
- No lateral branches in intestinal caeca
- Hermaphrodite
- Testes: 02 heavily branched testes, one behind other; in posterior 2/3rd of body behind ovary
- Ovary: fan-shaped, situated close to acetabulum
- Vitelline glands: Greatly branched, located along lateral margin of body
 Magnification x4
Magnification x4