Skip to content
- Disease: Schistosomiasis
- Habitat in human: Veins of the intestine ( S. mansoni & S. japonicum) or bladder (S. haematobium)
- Definitive host: Human
- 01 intermediate host only: Snails
- Diagnosis of infection: Microscopic examination of faeces (S. mansoni & S. japonicum) or urine (S. haematobium) for eggs
Morphological Features
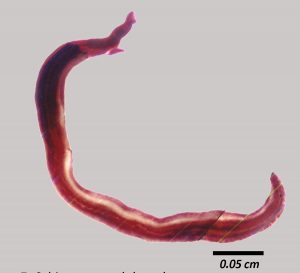
- Body is worm like- elongated and cylindrical
- Sexes are separate
- Female longer and more slender than male; vary from 7 – 26 mm depending on species
- Intestinal caecae reunite after bifurcation to form a single canal
- Shape: Worm-like elongated cylindrical bodies
- Both oral and ventral suckers present in an anterior position of body
- Intestinal caeca reunite after bifurcation to form a single canal
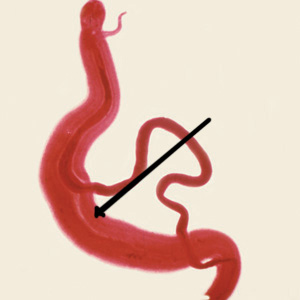
- Male has a groove called the gynecophoral canal (arrow) – female is held within this canal
 Male
Male
 Female
Female


