- Develops in lung, liver, etc., of intermediate host (sheep, cattle, human)
- Infective stage to the definitive host, i.e., dog
- Diagnosis of infection in human: Finding hydatid cyst via imaging and histological techniques or via immunological techniques that detect antibodies
Morphological Features
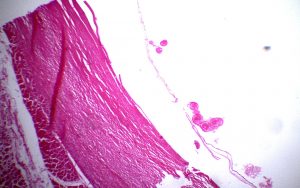
- Spherical fluid filled (hydatid fluid) structure
- Size: around 10 mm in diameter
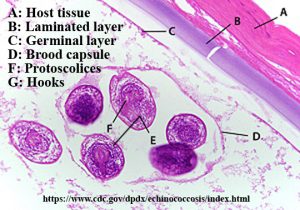
- Can observe endocyst and ectocyst
- Outermost ectocyst: Fibrous layer of host tissue; develops as a result of a host reaction
- Inner endocyst: Parasite origin; consists of a striated laminated layer and an inner germinal layer
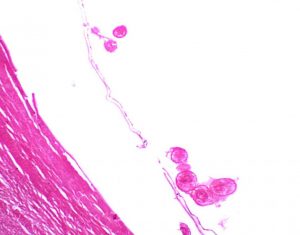
- Site of asexual reproduction: Germinal layer – produce brood capsules that bud off protoscolices
- Protoscolices: round to oval in shape; contain hooks – each protoscolex is a potential adult tapeworm
- Mature hydatid cysts may also form daughter cysts and granddaughter cysts
- Hydatid sand: Granular material in hydatid fluid that contains free protoscolices